Understanding Bursitis
14 January 2026
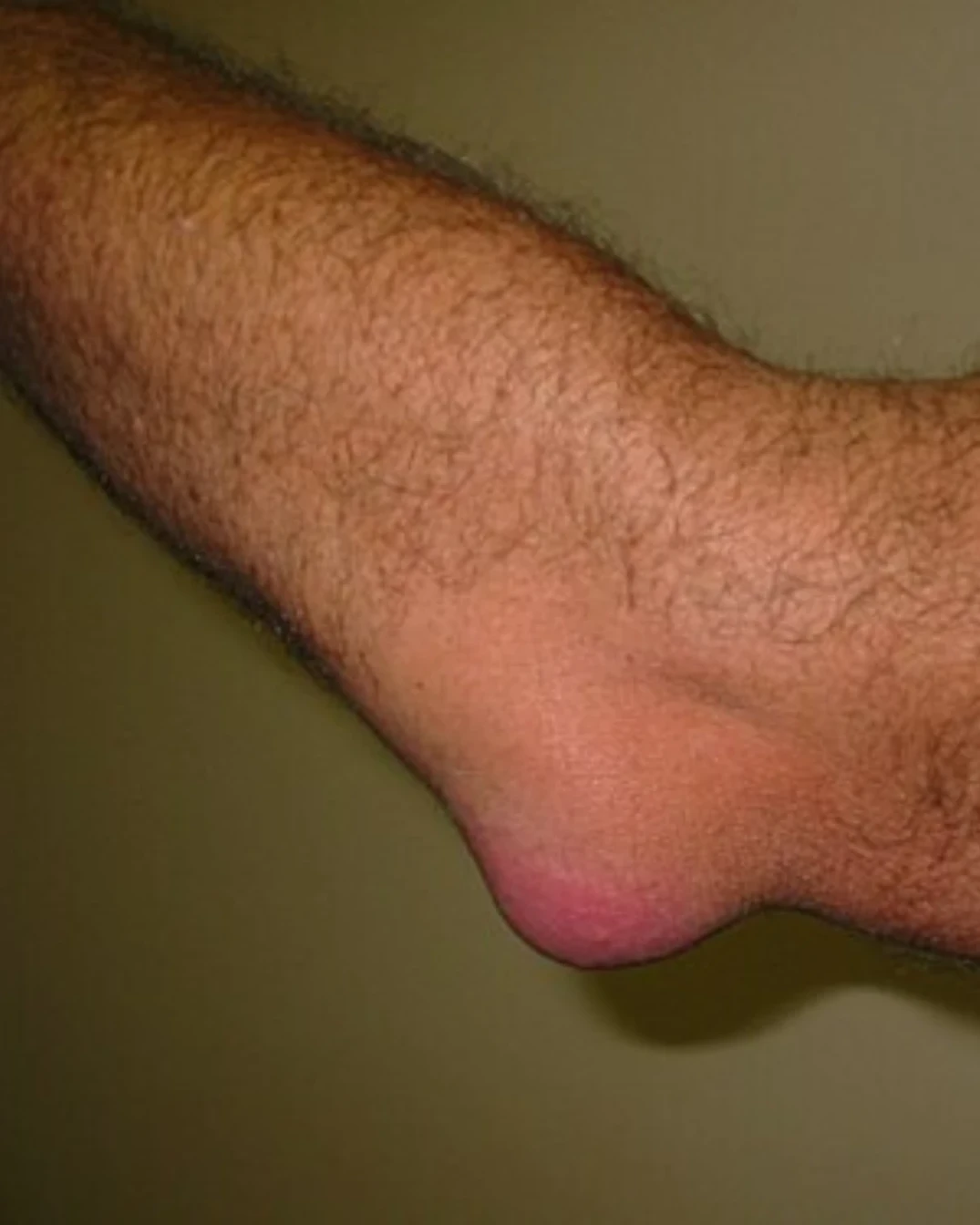
Understanding Bursitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Care
In wrapping up 2025, we concluded our discussions with an examination of shoulder injuries related to dislocations. To begin 2026, we will continue our mini-series approach with a new topic: Bursitis. In this blog post I will elaborate on the common symptoms and treatment options for bursitis. In subsequent posts, we will highlight some of the common places in the body where people can get bursitis, and discuss its management.
What Is Bursitis?
Bursitis is a common condition that can cause pain and sometimes limit movement. It generally occurs around joints that get a lot of use. Inside your body are small, fluid-filled sacs called bursa(e). These sacs act like cushions, reducing friction between bones, muscles, tendons and skin when you move. Bursitis happens when one of these bursae becomes inflamed, leading to pain and sometimes swelling near a joint.
What Causes Bursitis?
Several factors can lead to bursitis, and it can be experienced by any individual. Commonly, we see areas that undergo repetitive movements or prolonged pressure develop bursitis. Additionally, poor posture, improper technique during activities, and trauma – like sudden impact injuries, may also lead to the development of bursitis. Less commonly, underlying medical conditions and infections may cause bursitis.
Albeit not all-encompassing, some of the common areas we see bursitis develop in the body are the ankles, knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. In our future blog posts, each one of these areas will be addressed in detail.
Associated Symptoms of Bursitis
Symptoms of bursitis can vary depending on the individual, but commonly an individual may experience:
- Localized pain or tenderness near a joint
- Possible swelling or warmth in the affected area
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion around the affected joint
- Pain that worsens with movement or pressure
How Is Bursitis Managed?
Most cases of bursitis improve with activity modification, relative rest and avoiding aggravating factors that induce pain. Initially, as physiotherapists, we attempt to reduce pain and inflammation and restore normal movement. Subsequently, we identify the root cause of the bursitis and work to improve strength, flexibility, and/or correct faulty movement patterns to prevent recurrence. As symptoms improve, a gradual return to work/sports is advised with education on tools the individual may use for long-term success.
Conclusion
Bursitis can be uncomfortable, but with proper care and prevention, most individuals recover fully. Listening to your body, resting when needed, and practising healthy movement habits can go a long way in keeping your body strong and pain-free. If you believe you may have bursitis, consult with one of the physiotherapists at Kamloops Physiotherapy & Sports Injury Centre, as they can guide you through a specific, individualised rehabilitation program that will improve your chances of a full recovery. This blog post was written by physiotherapist Jacob Coelho. To book an appointment with Jacob or one of our other experienced therapists, call 250-314-0788 or book online HERE.
